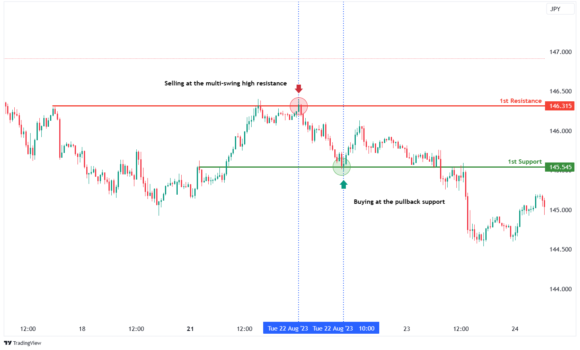
Trading in financial markets can be both exciting and challenging. To succeed, traders need clear strategies to navigate market ups and downs, manage risks, and maximize profits. In this guide, we’ll explore various trading strategies, their key components, and tips for implementing them effectively.
What Are Trading Strategies?
A trading strategy is a systematic approach to making trading decisions. It includes rules and guidelines that help traders determine when to buy or sell, how much money to risk, and what tools or indicators to use. A well-defined trading strategy helps traders avoid emotional decision-making and stay focused on their goals.
Key Components of a Trading Strategy
- Market Analysis: Understand the market conditions through technical or fundamental analysis.
- Entry and Exit Points: Define when to buy or sell an asset clearly.
- Risk Management: Establish rules for limiting losses and protecting capital.
- Position Sizing: Decide how much of your capital to allocate to each trade.
- Review and Adaptation: Continuously evaluate your performance and adjust your strategy as needed.
Common Trading Strategies
1. Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day. Traders aim to profit from small price movements by executing multiple trades throughout the day.
- Key Features:
- Requires significant time and market monitoring.
- Utilizes technical analysis and short-term indicators.
- Positions are closed before the market closes to avoid overnight risk.
- Tips:
- Focus on liquid markets with tight spreads.
- Use limit orders to ensure better pricing.
- Develop a disciplined routine and stick to it.
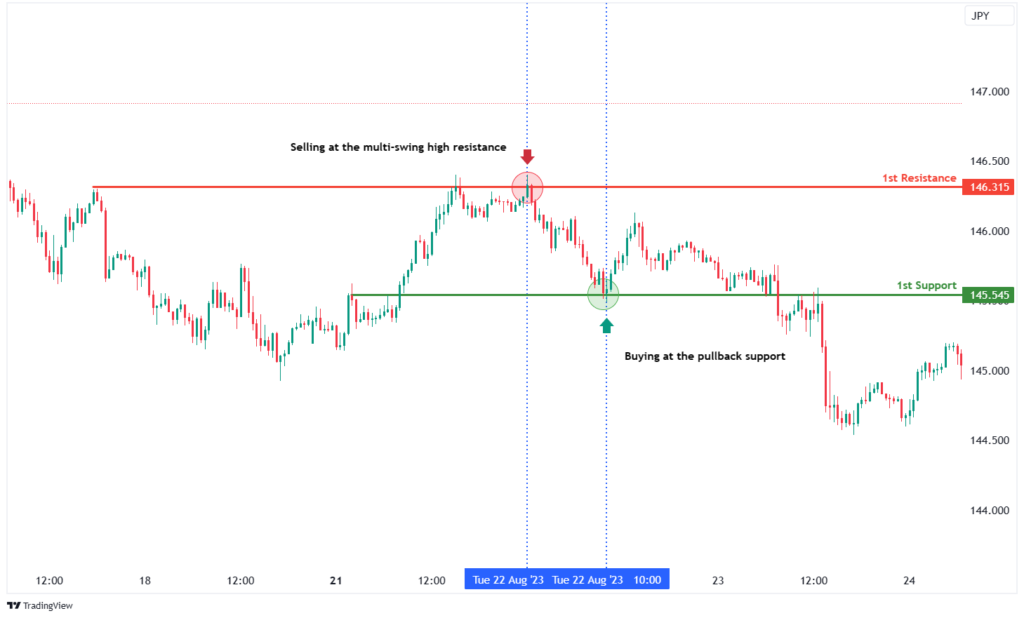
2. Swing Trading
Swing trading aims to capture price swings or trends over a few days to weeks. Traders use technical analysis to identify entry and exit points, holding positions longer than day traders.
- Key Features:
- Less time-intensive than day trading.
- Based on market momentum and trend reversals.
- A mix of technical and fundamental analysis is often used.
- Tips:
- Look for stocks or currency pairs with high volatility.
- Use tools like moving averages and RSI for signals.
- Set clear profit targets and stop-loss levels.
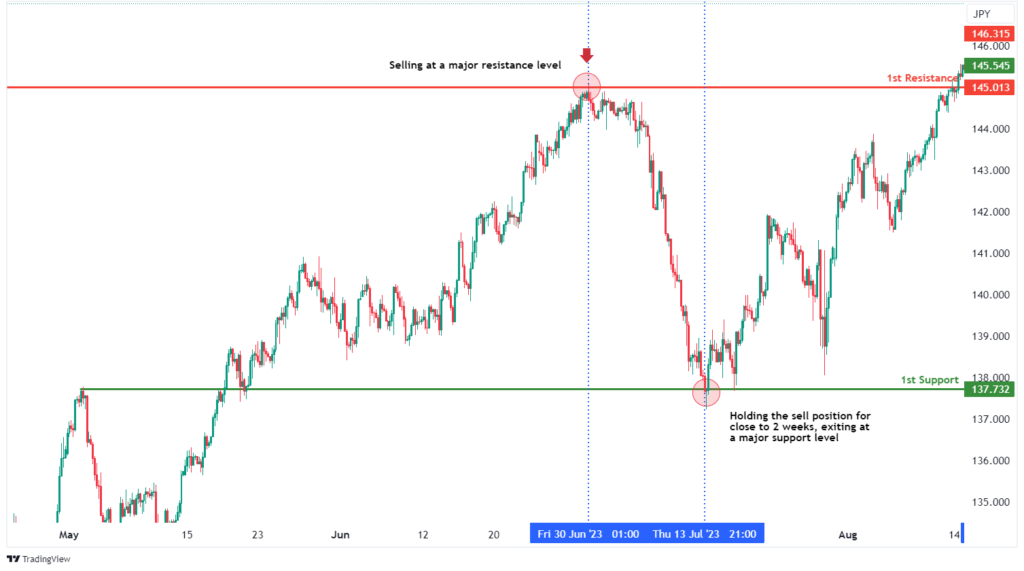
3. Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years. This approach relies on fundamental analysis and long-term trends.
- Key Features:
- Less affected by short-term market fluctuations.
- Involves in-depth analysis of economic indicators and company fundamentals.
- Requires patience and discipline.
- Tips:
- Focus on major economic trends and shifts.
- Diversify your portfolio to mitigate risks.
- Regularly review and adjust your positions as necessary.
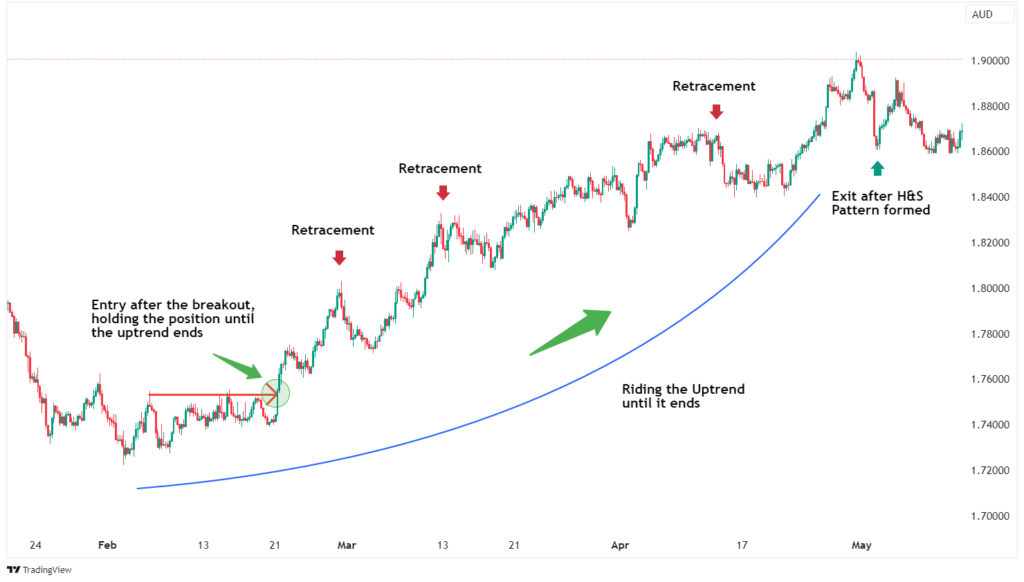
4. Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy that aims to profit from small price changes. Traders make numerous trades throughout the day, holding positions for just seconds or minutes.
- Key Features:
- Requires quick decision-making and execution.
- Focus on liquid markets with low spreads.
- Relies heavily on technical analysis and chart patterns.
- Tips:
- Use short time frames (1-5 minutes) for trading.
- Keep transaction costs low to maximize profitability.
- Develop a disciplined approach to manage trades effectively.
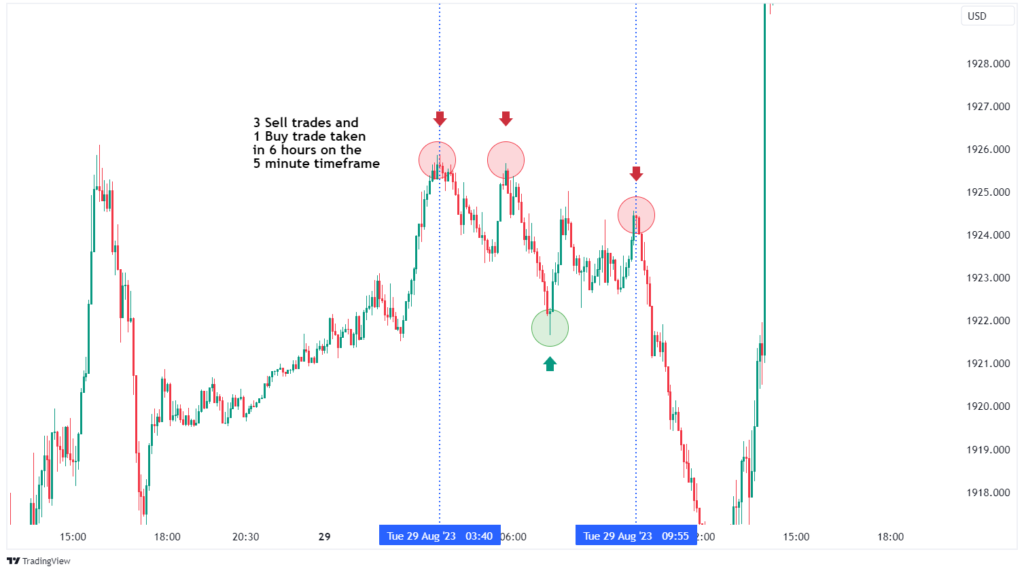
5. Trend Following
Trend following strategies involve identifying and following established market trends. Traders aim to enter positions in the direction of the trend, whether bullish or bearish.
- Key Features:
- Can be applied to various time frames (short-term to long-term).
- Uses technical indicators like moving averages and trendlines.
- Requires patience to ride out trends.
- Tips:
- Use trailing stops to protect profits as trends continue.
- Confirm trends with multiple indicators.
- Stay updated on market news and events that could affect trends.
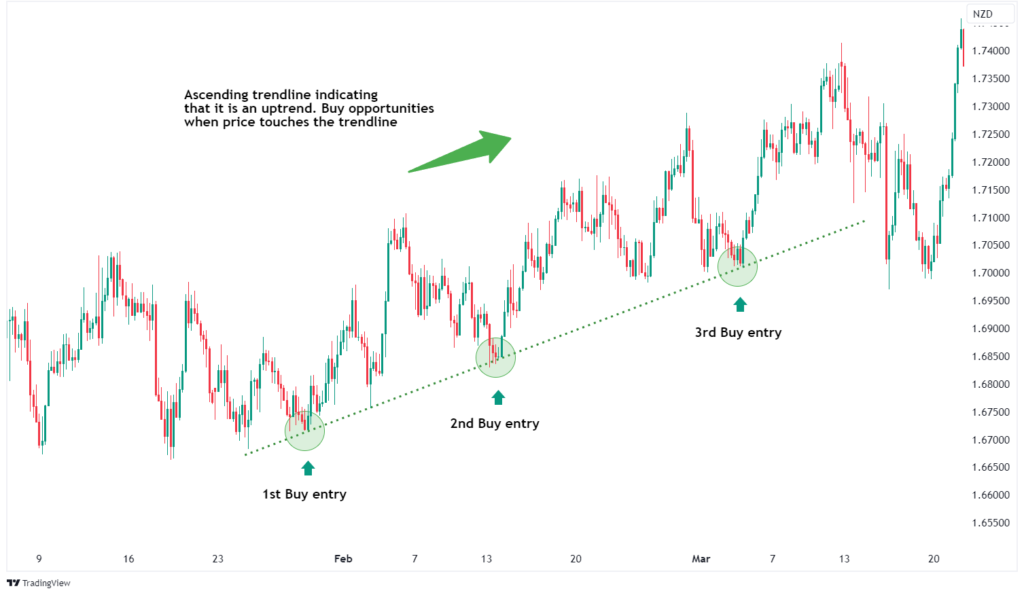
6. Breakout Trading
Breakout trading focuses on entering trades when the price breaks through established support or resistance levels. Traders aim to profit from the momentum that follows the breakout.
- Key Features:
- Identifying key price levels is essential.
- Often involves pre-breakout consolidation patterns.
- Can be applied in various market conditions.
- Tips:
- Confirm breakouts with high volume to avoid false signals.
- Use stop-loss orders to manage risk.
- Set profit targets based on volatility.
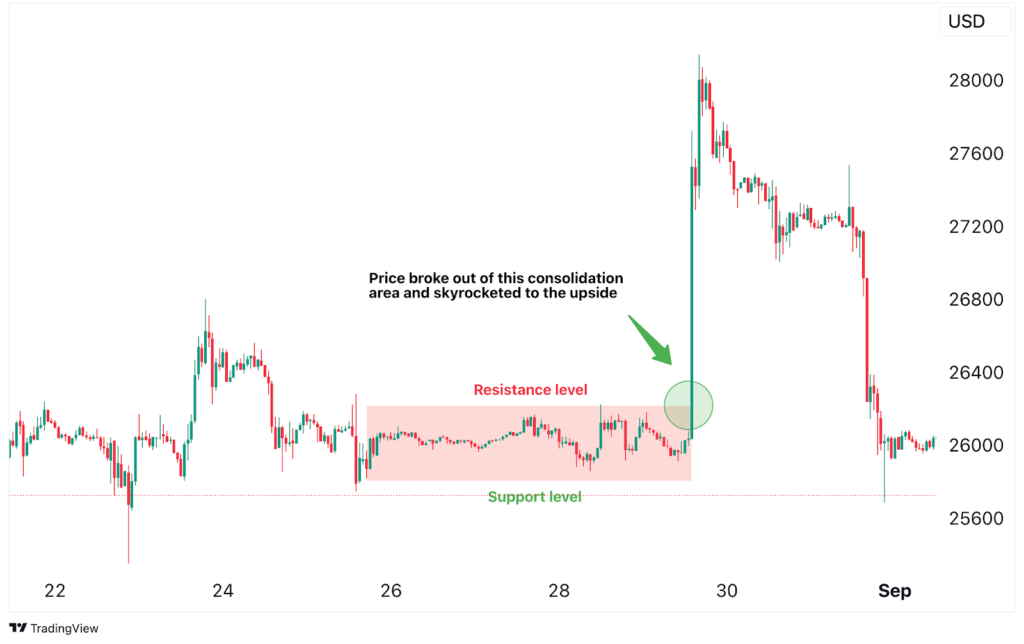
Risk Management in Trading Strategies
No trading strategy is complete without a solid risk management plan. Here are some key principles to follow:
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Always set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Avoid putting all your capital into a single asset or market.
- Position Sizing: Decide how much of your capital to risk on each trade based on your overall portfolio size.
- Avoid Over-Leveraging: Use leverage cautiously, as it can amplify both profits and losses.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly assess your performance and adapt your strategy as needed.
Conclusion
Developing an effective trading strategy is crucial for success in the financial markets. By understanding different trading strategies and incorporating strong risk management practices, traders can enhance their decision-making and increase their chances of profitability. Remember that continuous learning, practice, and adaptation are key to becoming a successful trader in any market environment. Whether you choose day trading, swing trading, or any other strategy, always stay disciplined and informed to navigate the complexities of trading effectively.